
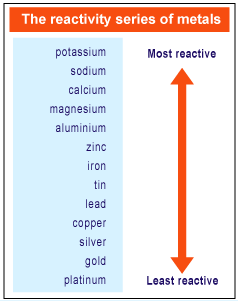
These differences in reactivity depend on where an element is placed in the periodic table. How are metals and non-metals react on the periodic table? Groups Type Pattern of reactivity 1, 2, 3: Metal: Reactivity increases down the group: 5, 6, 7: Non-metal: Reactivity decreases down the group What are the types of reactivity in the periodic table? Reactivity increases as we move from left to right across a period or moving towards non-metals from metals , When does reactivity increase as you move from left to right? All alkali metals have one electron in the outer shell. The electron shells between the outer electrons and the nucleus have a ‘shielding’ effect which reduces the attraction of the outer electrons to the nucleus. The number of shells of electrons also increases. How does the reactivity of Group 1 metals change?Īs you go down a group the atomic number increases. Sodium and potassium both play an important role in biological life on Earth. Cesium clocks are considered the most accurate of all clocks. Cesium and rubidium are used to make atomic clocks. What are the two most important alkali metals Why are they important?īecause they are so reactive with air and water, they are generally stored in oil. Group – reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Period – reactivity increases as you go from the left to the right. Period – reactivity decreases as you go from left to right. What is the trend in reactivity on the periodic table? Lithium, sodium, and potassium all react with water, for example. The elements toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table are the metals that are the most active in the sense of being the most reactive. The primary difference between metals is the ease with which they undergo chemical reactions. How do you know which elements are more reactive?
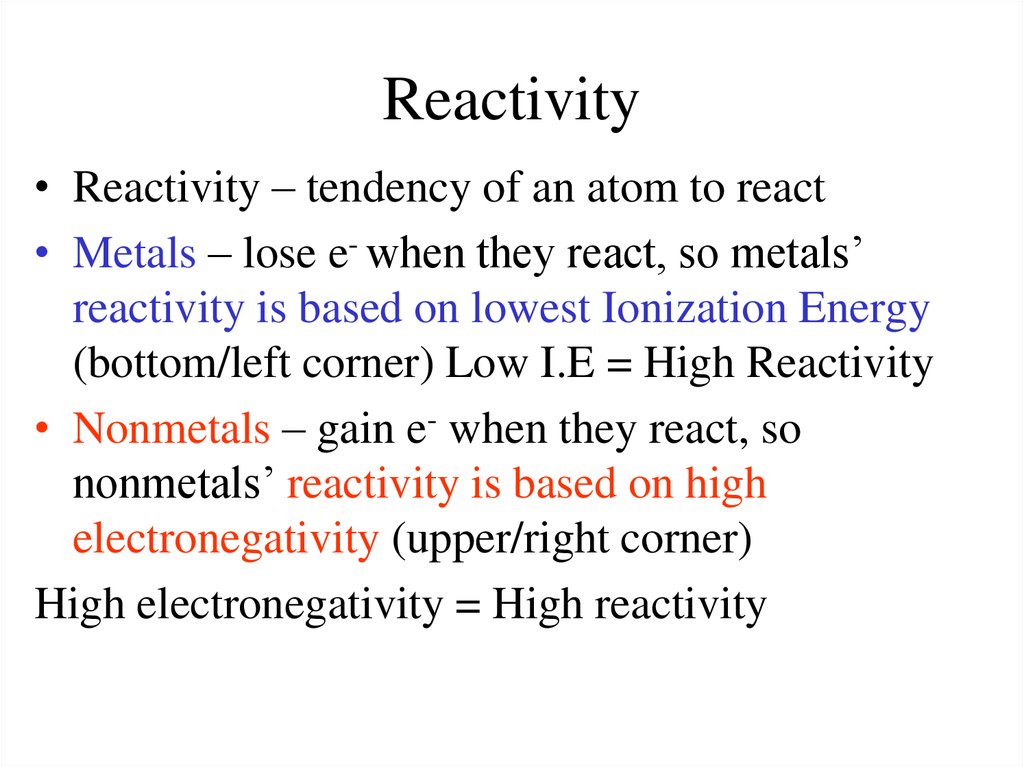
What is the trend as you move from top to bottom in a group regarding the reactivity of metal? The reactivity all increases as you go down the periodic table, for example rubidium is far more reactive than sodium. Each element going from left to right tends to be more reactive. Reactivity: The reactivity of the elements increases going from left to right on the periodic table. Is there a correlation between reactivity of elements and their position in the periodic table? the attraction between the nucleus and outer electron gets weaker as you go down the group – so the electron is more easily lost. The reactivity of Group 1 elements increases as you go down the group because: the outer electron gets further from the nucleus as you go down the group. How does reactivity change as you go down the table?

reactivity of metals decreases from left to right.

What happens to the reactivity of metals from left to right across the periodic table? as you go across a period, the number of valence electrons increases. What happens to the reactivity of metals as you move from left to right on the table? How does the reactivity of metals change as you move down and column and across a group?Įxplanation: As you go down a column (group or family) on the periodic table, the reactivity of metals increases. The farther to the left and down the periodic chart you go, the easier it is for electrons to be given or taken away, resulting in higher reactivity. How does reactivity change across the periodic table for metals?Ĭhemical reactivity of the elements – definition Period – reactivity decreases as you go from left to right across a period. 5 How are metals and non-metals react on the periodic table?.4 How does the reactivity of Group 1 metals change?.3 How do you know which elements are more reactive?.2 How does reactivity change as you go down the table?.1 How does reactivity change across the periodic table for metals?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
